May 3, 2011
How Do I Consider Welded Aluminum Connections in RISA-3D?
In Aluminum design, the welded areas have a decreased material strength and RISA-3D can assign any material strength to the members based on the Material spreadsheet.
Powerful Tools Don’t Help If They’re Left Unused Many engineers evaluate analysis software based on core modeling and design checks. But once a demo is over, some of the most impactful features are the ones that quietly save time on real projects — especially mid-size jobs where efficiency matters most. These aren’t advanced edge-case tools. They’re everyday features that often go underused. Diaphragm Forces: See Load Paths Instead of Guessing Diaphragm force output is one of the most valuable — and least leveraged — parts of a full building model. Instead of relying on manual distribution or conservative assumptions, engineers can directly see how loads are flowing to vertical elements. For mid-size structures, this clarity can mean: Fewer overdesigned collectors More confidence in lateral load paths Faster review and revisions when layouts change Batch Results: Review Smarter, Not Longer Batch results allow engineers to review multiple load cases, members, or design checks in a single pass. Instead of hunting through individual reports, patterns become obvious quickly. On mid-size jobs, this speeds up: QA/QC reviews Iterative design changes Comparing “before and after” scenarios It’s not about skipping checks — it’s about seeing the full picture sooner. Design Iteration Speed Is the…
Read More

In Aluminum design, the welded areas have a decreased material strength and RISA-3D can assign any material strength to the members based on the Material spreadsheet.
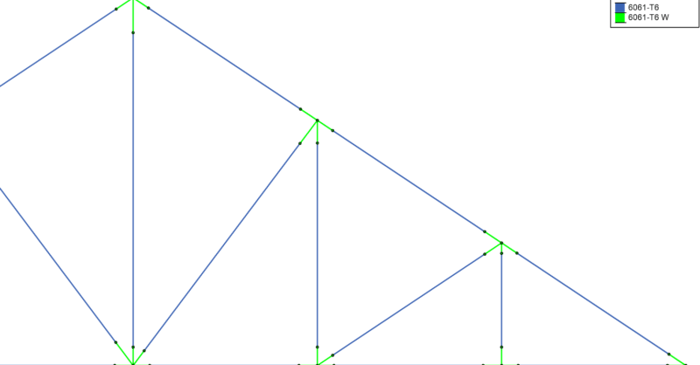
After solving a model with Member Area Loads, RISA-3D will automatically create Transient Basic Load Cases that allow the user to verify load distribution.
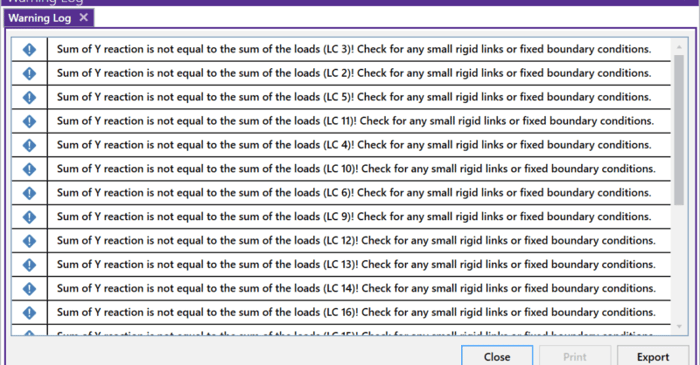
RISA-3D will now check your model for errors by summing the reactions in your model and comparing them to the applied loads. This occurs for the global X, Y, and Z directions. If RISA identifies that the reactions do not equal the applied loads then the software will show a warning message to the...
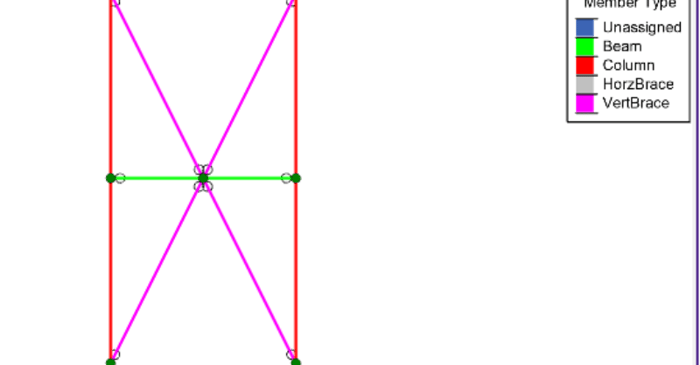
In RISA-3D, there are many different applications that require you to define Member Type in your model including AISC 15th Edition steel design, Seismic Design, Concrete design, and models that will be transferred to Autodesk Revit.
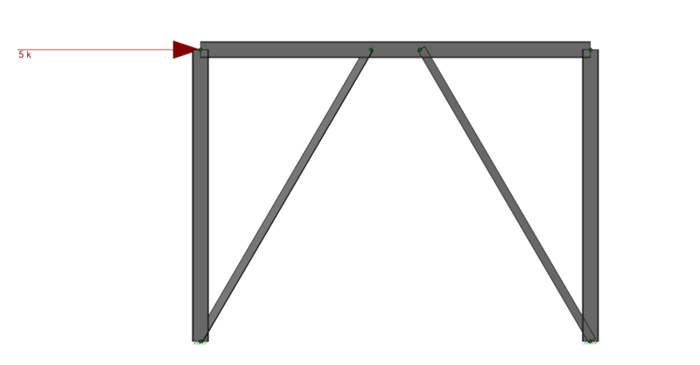
V-Brace frames in RISA-3D seismic design have unbalanced forces shown on both the beams and braces. As brace frames displace under lateral loads, one brace will buckle and its force decreases while the other brace in tension will have an increase of force until it reaches yield.
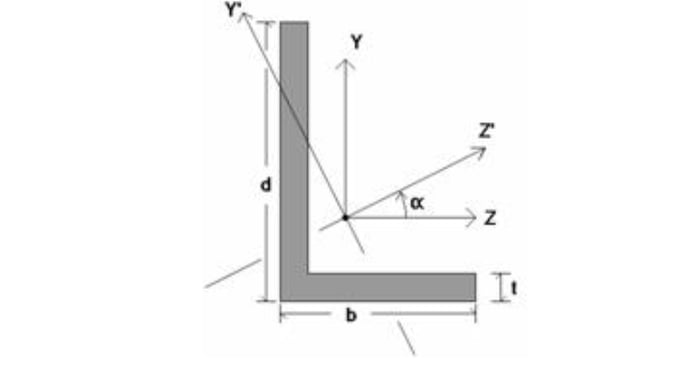
The bending and axial code checks for single angles differ somewhat from other shape types, because single angles behave quite differently in bending and compression depending on how they are braced along their length.

The Seismic Provisions in RISA-3D will check various design and code check requirements according to the AISC design provisions (AISC 360-2005, AISC 341-2005, AISC 358-2009). Seismic Design Rules can be applied to any member in the model, just follow the steps listed below.
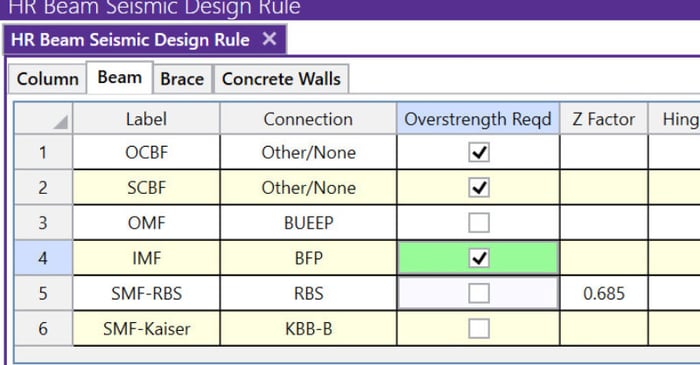
The Seismic Design rules can be found in RISA-3D on the Data Entry toolbar or in the Spreadsheets menu. Below is a quick-reference description of the entries required. For further information refer to the Online Help File > Seismic Detailing.
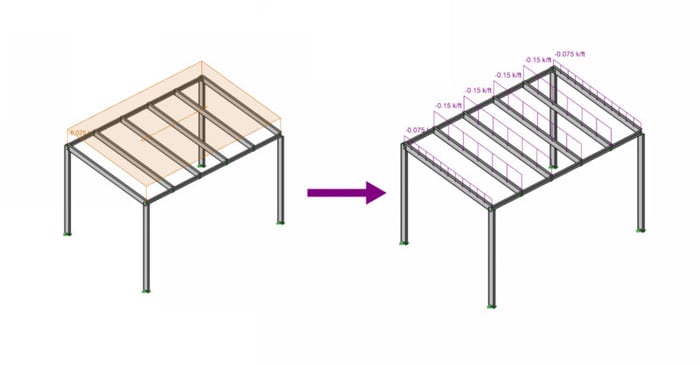
When a model is solved that contains Member Area Loads, the program automatically attributes them to the applicable members within the defined area of the applied load. The load is attributed to the members as distributed loads that RISA-3D defines as Transient Loads.
Our monthly "Structural Moment" newsletter is the best way to keep up with RISA’s product updates, new releases, new features, training events, webinars and more...