Why Are The Steel Beam Deflections So Large?
When solving a RISA-3D model with hot rolled steel members under the...
When a model is loaded, it deflects. The deflections in the members of the model may induce secondary moments due to the fact that the ends of the member may no longer be vertical in the deflected position. These secondary effects for members can be accurately approximated through the use of P-Delta analysis.
This type of analysis is called “P-Delta” because the magnitude of the secondary moment is equal to “P”, the axial force in the member, times “Delta”, the distance one end of the member is offset from the other end.
Step 1: The model is loaded with the Applied loads (P shown above)
Step 2: The model deflects Δ, and the secondary shear force (V) is calculated for every member;
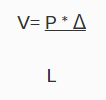
Step 3: The model is re-solved (internally) with the secondary shear forces applied (V shown above).
Step 4: The displacements for this new solution are compared to those obtained from the previous solution. If they fall within the convergence tolerance, the solution has converged. If not, return to Step 2 and repeat.
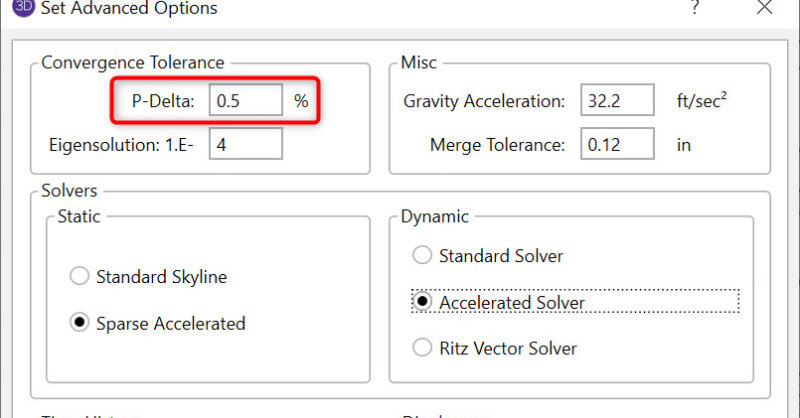
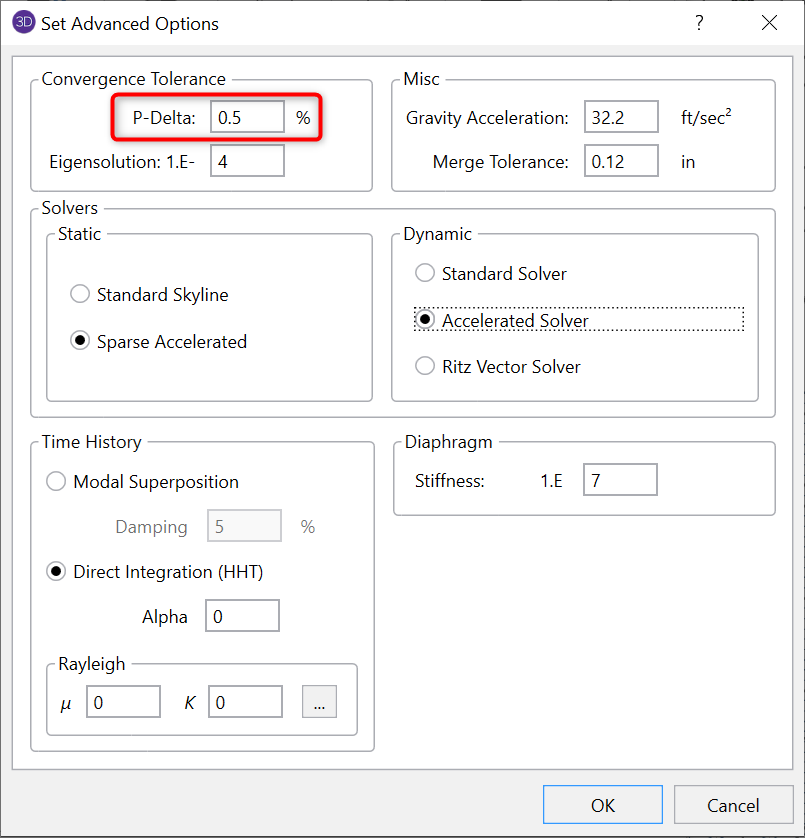
The convergence tolerance is found in the Model Settings and is set by default to 0.5%.
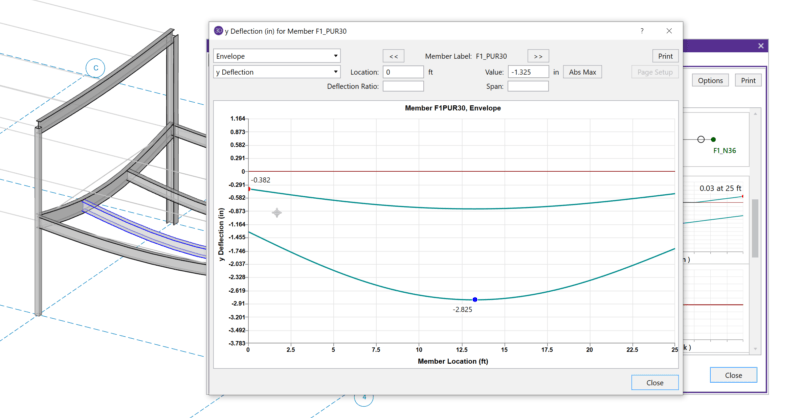
When solving a RISA-3D model with hot rolled steel members under the...
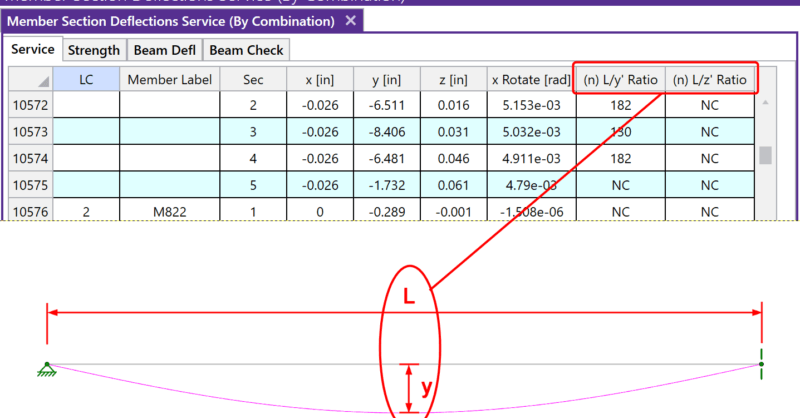
After solving a model, you will see in the Member Deflections...
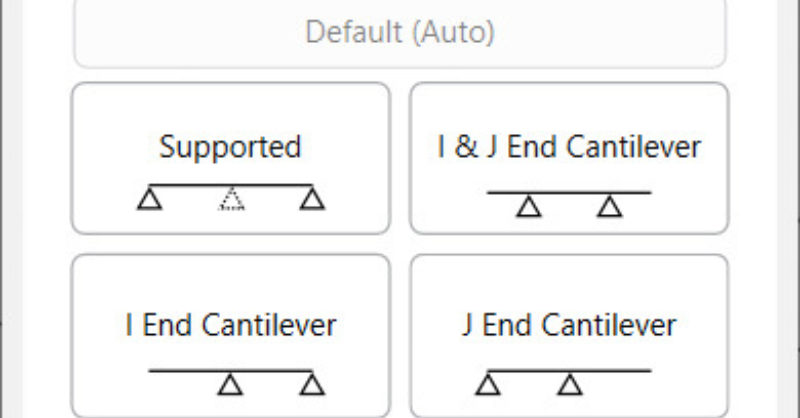
RISA-3D v16.0.4 introduces an enhancement that will allow for more...