June 28, 2011
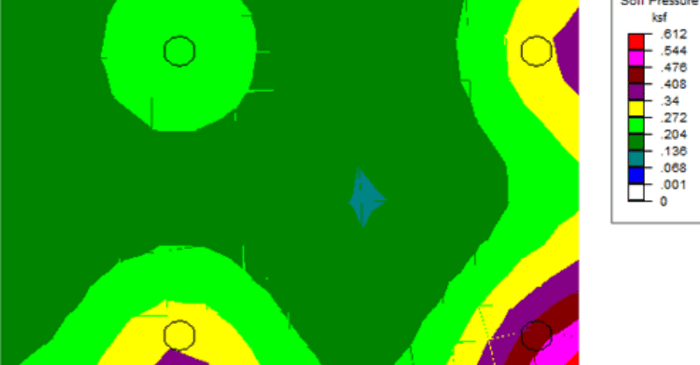
Checking Soil Bearing in RISAFoundation
RISAFoundation has the capability to report soil bearing pressures, and check them against allowable pressures.
Powerful Tools Don’t Help If They’re Left Unused Many engineers evaluate analysis software based on core modeling and design checks. But once a demo is over, some of the most impactful features are the ones that quietly save time on real projects — especially mid-size jobs where efficiency matters most. These aren’t advanced edge-case tools. They’re everyday features that often go underused. Diaphragm Forces: See Load Paths Instead of Guessing Diaphragm force output is one of the most valuable — and least leveraged — parts of a full building model. Instead of relying on manual distribution or conservative assumptions, engineers can directly see how loads are flowing to vertical elements. For mid-size structures, this clarity can mean: Fewer overdesigned collectors More confidence in lateral load paths Faster review and revisions when layouts change Batch Results: Review Smarter, Not Longer Batch results allow engineers to review multiple load cases, members, or design checks in a single pass. Instead of hunting through individual reports, patterns become obvious quickly. On mid-size jobs, this speeds up: QA/QC reviews Iterative design changes Comparing “before and after” scenarios It’s not about skipping checks — it’s about seeing the full picture sooner. Design Iteration Speed Is the…
Read More

RISAFoundation has the capability to report soil bearing pressures, and check them against allowable pressures.
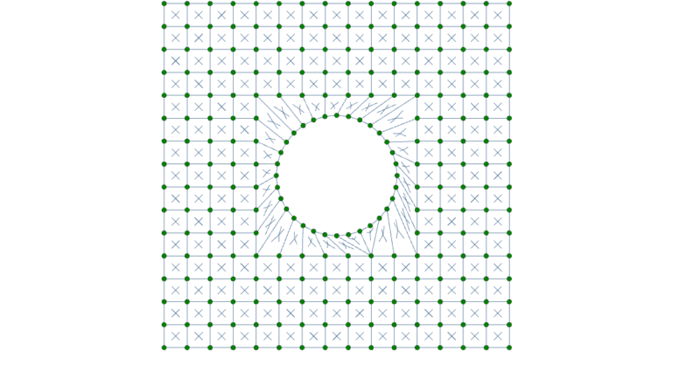
While RISA-3D (or RISA-2D) does not have an explicit tool to punch a hole in a plate, you can use the following steps to manually model them:
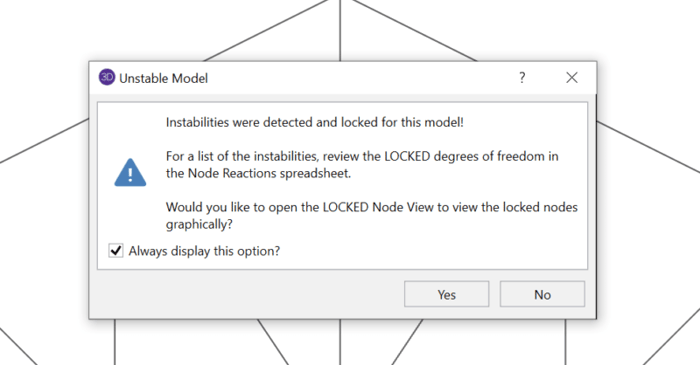
Have you ever received an instability warning when running a three dimensional RISA-3D model? This is because RISA-3D cannot build the stiffness matrix with the configuration you have modeled. In some cases, your model is truly unstable and in others it’s a matter of correctly modeling your...

In RISAFloor on the roof level, you layout only the top chords of the truss and create your slope. These top chords by themselves probably won’t be sufficient enough to get designed in RISAFloor, but, don’t worry, we’ll take care of that in RISA-3D when we model the rest of truss.
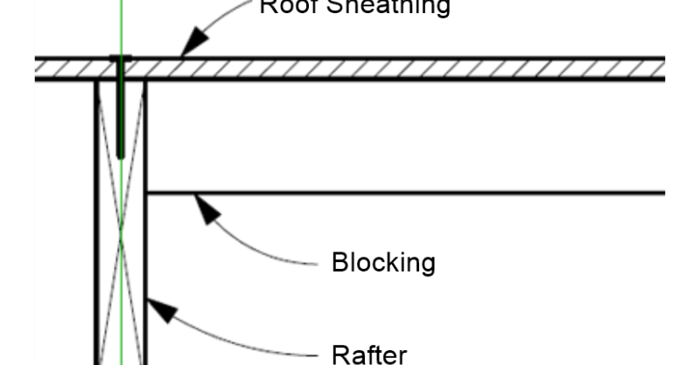
In RISAFloor, the beams are susceptible to two forms of buckling; Euler buckling and lateral-torsional buckling. The unbraced length is determined in RISAFloor using the deck properties and framing.
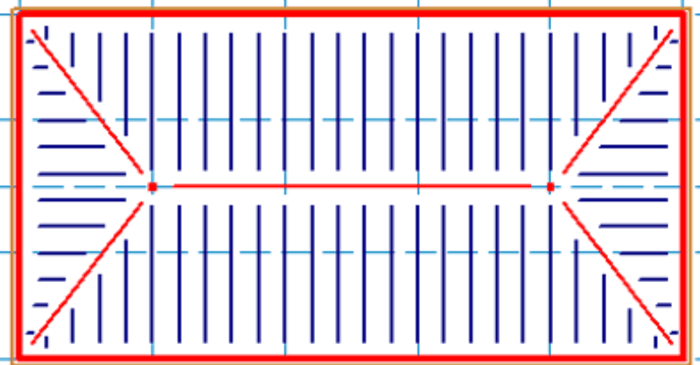
Using this method in RISAFloor, we are not actually designing the trusses, but just adding “dummy” bottom and top chords to correctly calculate the loading and help distribute the loads to the walls.
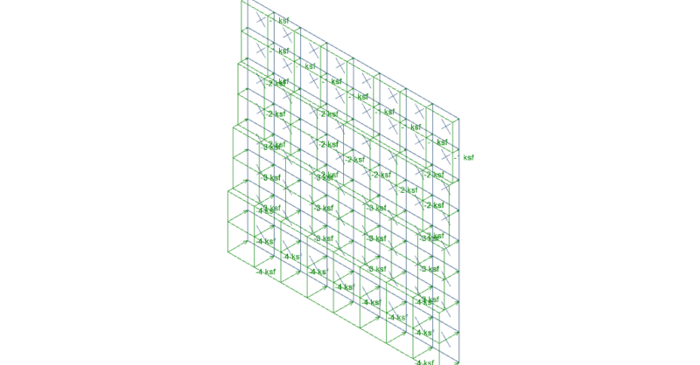
It’s easy to apply tapered surface loads to plates in RISA-3D by stepping up the loads from one level to the next.
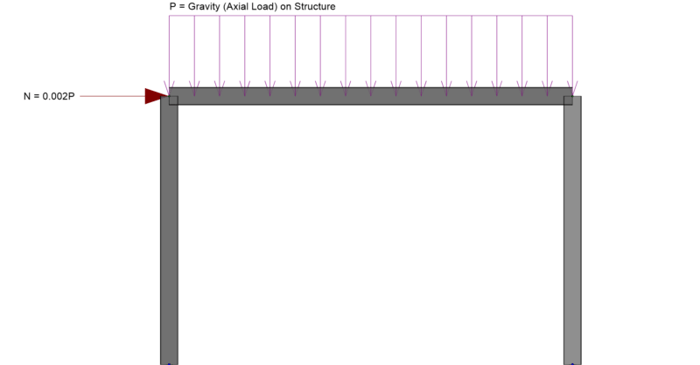
In RISA-3D you can automatically apply notional loads to your structure to comply with your steel code (such as AISC 360). Notional loads take into account a building’s actual out-of-plumbness by adding de-stabilizing lateral loads. The AISC 360 recommends either 0.2% or 0.3% of the vertical loads...
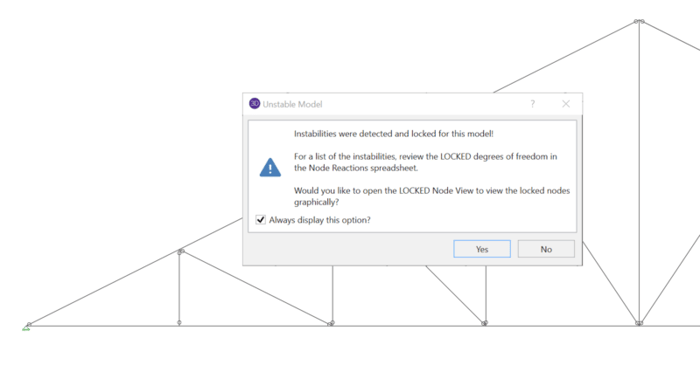
When running a truss model in RISA-3D or RISA-2D, it’s quite common to receive an instability warning, but these can be easily resolved by following a few simple rules.
Our monthly "Structural Moment" newsletter is the best way to keep up with RISA’s product updates, new releases, new features, training events, webinars and more...