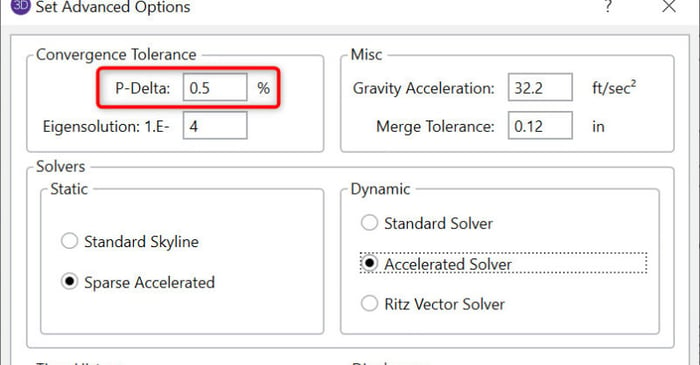
March 9, 2011
How Do I Investigate My RISA-3D Model Using the Deflected Shape?
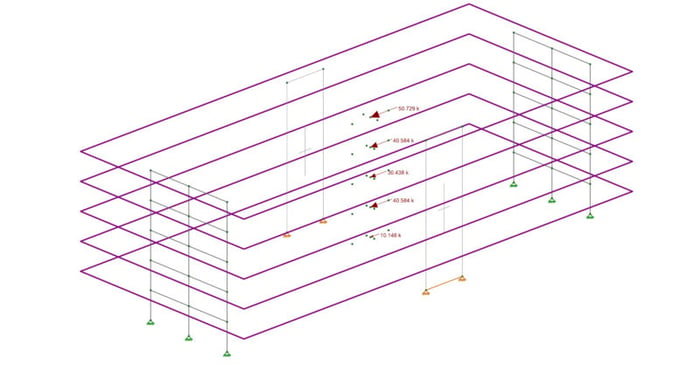
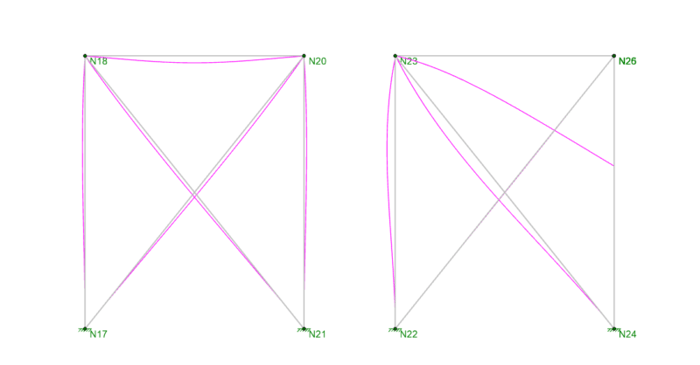
When your RISA-3D model is not behaving as you anticipated, one of the best tools you have is viewing the deflected shape. Displaying the deflection graphically will help you visualize how the model is behaving and will often times bring to light modeling errors.