AISC 341-16 & AISC 358-16 now included in RISA-3D
The AISC 341-16 and AISC 358-16 Edition changes have been implemented into...
Structural engineering isn’t just about calculations—it’s about making assumptions explicit, validating them against the built environment, and translating loads into actionable design decisions. Even perfect analysis won’t prevent problems if coordination fails. Here are four real-world cases that illustrate the challenges and solutions that practicing engineers face daily. Architect Coordination – “The Wall Section That Didn’t Exist” Project: Multi-story mixed-use building Challenge: The architectural drawings specified a wall section that was shallower than required for structural framing. Technical Issue: The structural model indicated that full lateral loads required a thicker wall cavity to properly anchor the framing. If built per the architectural drawings, the wall would have created clearance issues and compromised the lateral load path. Solution & Workflow: Compared architectural sections to the structural model in 3D. Highlighted discrepancies in the model and prepared annotated visuals. Shared a clear summary with the architect outlining why the wall depth needed adjustment. Outcome: The architect revised the wall section prior to construction. No field conflicts occurred, and the project stayed on schedule. Engineering Lesson: Always validate architectural assumptions against your structural model. Small dimensional mismatches can create drift, clearance, or lateral capacity problems. Contractor Coordination – “The Footing That Wasn’t There”…
Read More

The AISC 341-16 and AISC 358-16 Edition changes have been implemented into...

Cold-formed steel framing is a durable, reliable and cost-effective option...

The ability to apply a scaling factor to an entire Basic Load Case in the...

The new ACI 318-19 code has been implemented into RISA-3D v19, RISAFloor...

Recent tests and analytical results for concrete columns have indicated...

Watch the recording of our webinar to learn how new versions of RISA-3D,...

The Quick Start Course is a 4-hour introduction to the basic features and...
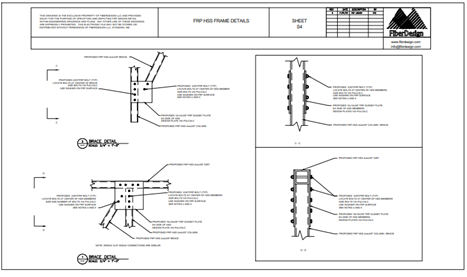
Overview FRP or Fiber Reinforced Polymer (thermoset) composite materials...

If you have utilized Hold-Down's in RISA-3D, you have mostly likely...
Our monthly "Structural Moment" newsletter is the best way to keep up with RISA’s product updates, new releases, new features, training events, webinars and more...