
July 2, 2021
Improved Functionality in ADAPT-Builder v20.0.1
The latest release of ADAPT-Builder (Version 20.0.1) includes improvements to model input, colorization and result display.
Powerful Tools Don’t Help If They’re Left Unused Many engineers evaluate analysis software based on core modeling and design checks. But once a demo is over, some of the most impactful features are the ones that quietly save time on real projects — especially mid-size jobs where efficiency matters most. These aren’t advanced edge-case tools. They’re everyday features that often go underused. Diaphragm Forces: See Load Paths Instead of Guessing Diaphragm force output is one of the most valuable — and least leveraged — parts of a full building model. Instead of relying on manual distribution or conservative assumptions, engineers can directly see how loads are flowing to vertical elements. For mid-size structures, this clarity can mean: Fewer overdesigned collectors More confidence in lateral load paths Faster review and revisions when layouts change Batch Results: Review Smarter, Not Longer Batch results allow engineers to review multiple load cases, members, or design checks in a single pass. Instead of hunting through individual reports, patterns become obvious quickly. On mid-size jobs, this speeds up: QA/QC reviews Iterative design changes Comparing “before and after” scenarios It’s not about skipping checks — it’s about seeing the full picture sooner. Design Iteration Speed Is the…
Read More

The latest release of ADAPT-Builder (Version 20.0.1) includes improvements to model input, colorization and result display.
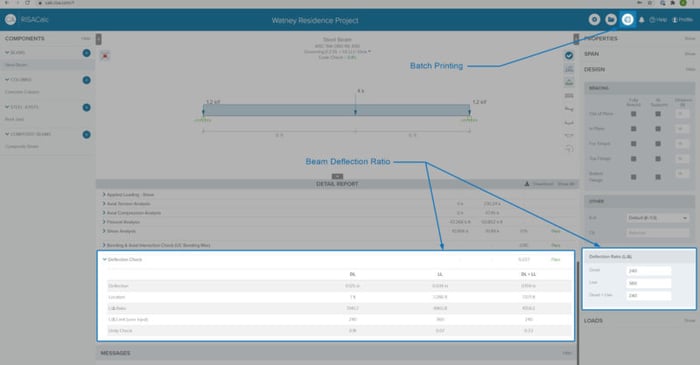
As our team is hard at work updating and improving RISACalc based on customer feedback and requests. This latest release (Version 2.1) now includes two new features; deflection ratio checks for beam components and batch report printing.

Over the past few years, RISA has been involved with Stand Up for Kids - Orange County. Since 2003, Stand Up for Kids has focused on putting an end to the cycle of youth homelessness in the community. They work to provide basic needs, housing, mentoring support, care, and love to at-risk and...
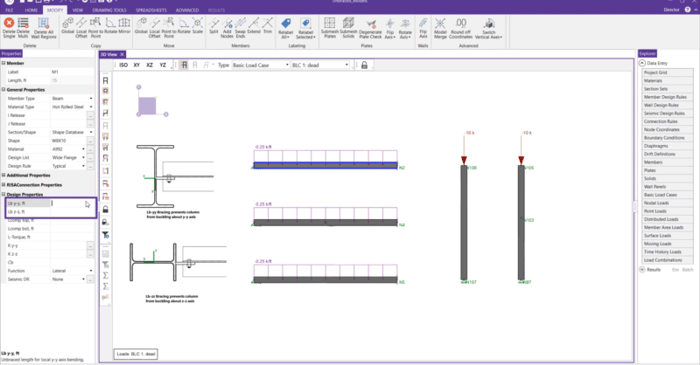
In this video, learn about the various unbraced length parameters that exist in RISA-3D and how the different values can impact the design of beam and column members in RISA-3D. Click the button below to navaigate to the RISA-3D Help File. Search: Unbraced Length.

Samiul Alam is an Applications Engineer at RISA and has been with the company since December 2020. After receiving a BS in Civil Engineering from UC Irvine and a Master of Engineering in Structural Design from USC, he held roles as a design, project, and lead engineer designing and analyzing a...
When a steel joist has special loading that requires extra consideration, the most economical solution may be to use a standard joist that is capable of resisting the non-standard or special loading. When this type of design arises, RISAFloor will add an (SP) extension to the joist designation in...

RISA software is staying current with all the Windows updates in order to bring you the best quality that Windows recommends. Unfortunately, that means it will require a little extra time during installation and your computer could require a reboot more than once. The current versions of RISA...
The ability to design buckling restrained braced frames has been added to RISA-3D when you integrate your model from RISAFloor. In collaboration with CoreBrace, this new feature came as part of the release of RISA-3D v19.0.0 and RISAFloor v15.0.0.
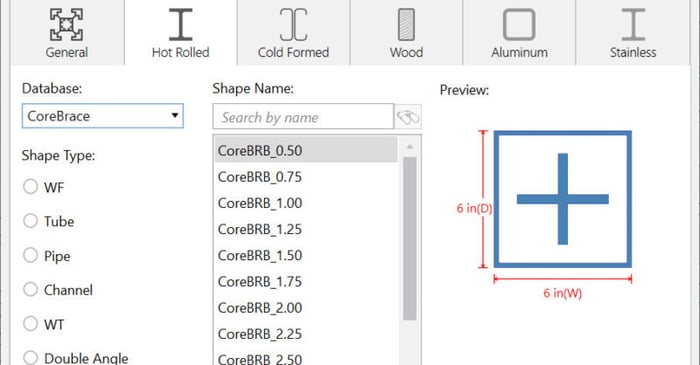
The ability to design buckling restrained braced frames has been added to RISA-3D when you integrate your model from RISAFloor. In collaboration with CoreBrace, this new feature came as part of the release of RISA-3D v19.0.0 and RISAFloor v15.0.0.
Our monthly "Structural Moment" newsletter is the best way to keep up with RISA’s product updates, new releases, new features, training events, webinars and more...