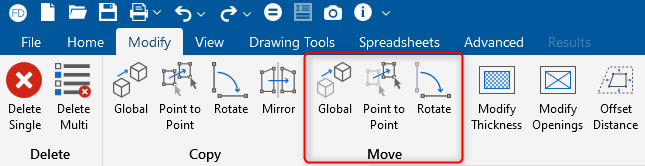
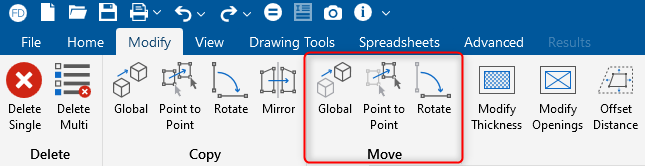
Enhanced "Move" Tools in RISAFoundation
RISAFoundation includes the added ability to move selected foundation...
Incorporating RISAFoundation into your foundation design process is more than just a time-saver—it’s a powerful tool for enhancing the accuracy and quality of engineering deliverables. By automating the most tedious and error-prone aspects of foundation design, RISAFoundation enables engineers to focus on solving complex challenges and developing innovative solutions. Check out some real-world applications where RISAFoundation could be used to streamline workflows and automate critical tasks, making projects more efficient and reliable.
1. High-Rise Building Foundations in Seismic Zones
Consider a project involving a high-rise building located in a seismic region, where the foundation must resist both vertical and lateral forces. In this scenario, an engineering team could leverage RISAFoundation to model a 20-story building's foundation. With automated load combination handling and the seamless integration of lateral forces imported from RISA-3D, the team would be able to evaluate various design options efficiently. By analyzing detailed outputs, they could optimize the thickness and reinforcement of a mat foundation, meeting seismic requirements while saving on materials.
2. Large Industrial Equipment Foundations
Imagine a foundation design for a large industrial project requiring support for high-capacity equipment, such as a crane at a port facility. In this case, RISAFoundation would allow engineers to incorporate substantial point loads and analyze repetitive dynamic stresses from crane operations. The software’s real-time load adjustment capabilities would enable quick adjustments to deflection outcomes, allowing for prompt refinements. With RISAFoundation, an engineering team could ensure a structurally sound foundation design that balances safety and material efficiency.
3. Multi-Building Podium Slab Design
For a multi-use development with a podium slab design, engineers might need to account for complex load distribution and potential soil settlement. With RISAFoundation, a team could simulate the podium slab and design the column supports to balance these forces. The software’s soil settlement analysis feature would allow them to evaluate the slab’s long-term performance and identify points requiring reinforcement. This approach would lead to a cost-effective foundation design with optimized rebar distribution, achieving construction cost savings without sacrificing stability.
Learn more about how to create and analyze real models like these for yourself in our on-demand RISAFoundation Quick Start course below
RISAFoundation offers robust functionality for designing a wide range of foundation systems—spread footings, mat foundations, combined footings, grade beams, and more. In traditional workflows, designing foundations can become labor-intensive, especially when managing interdependent elements like load combinations, settlement, uplift, and even soil-structure interactions. RISAFoundation’s automation capabilities handle these complexities with ease by:
Efficient Load Combination Handling: The software automatically integrates load combinations from RISA-3D and RISAFloor, reducing manual entry and error potential. Engineers can effortlessly analyze worst-case scenarios, factoring in gravity, lateral, and seismic loads, while focusing on the overall stability of the structure.
Precise Settlement Analysis and Reinforcement Calculation: RISAFoundation’s analysis engine can determine the optimal reinforcement layout, minimizing material use while meeting code requirements. The settlement analysis feature also accounts for varying soil properties, ensuring realistic foundation performance under all load conditions.
Soil Structure Interaction Modeling: For complex projects with varying soil profiles, RISAFoundation incorporates soil-structure interaction models that adapt to multiple soil types, slopes, and bearing capacities. This level of detail gives engineers a realistic view of how the foundation will perform, providing essential insights to inform decisions and mitigate risks in design.
RISAFoundation includes the added ability to move selected foundation...
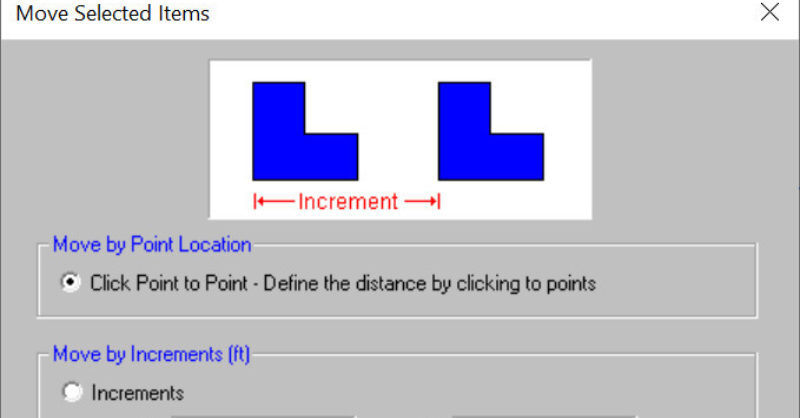
RISAFoundation v10.0 now includes the added ability to move selected...
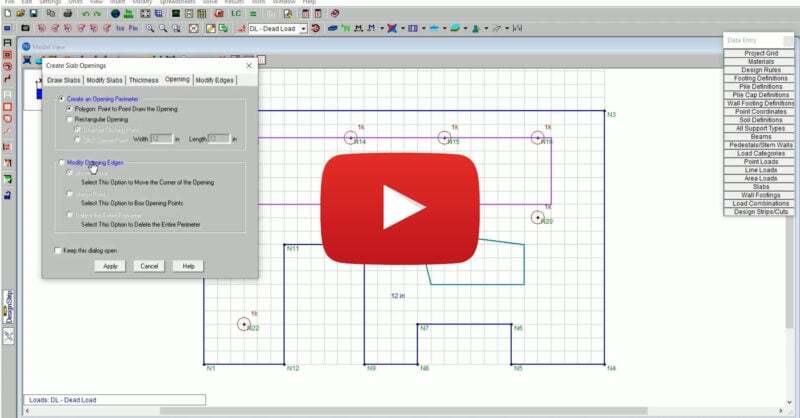
RISAFoundation Version 14 includes new and improved tools for the...