Methods to Integrate with RISAConnection
There are several ways to take your RISA-3D or RISAFloor model to...
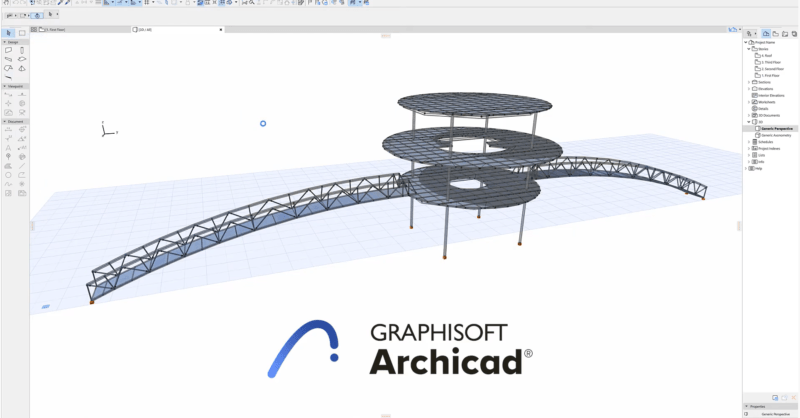
Learn how Graphisoft and RISA are working together to leverage model information created by the architect to create a more seamless workflow, while minimizing the duplication that is typical of today's design process:
| Feature | ADAPT-PT/RC | ADAPT-Builder |
|---|---|---|
| Preliminary Sizing | X | X |
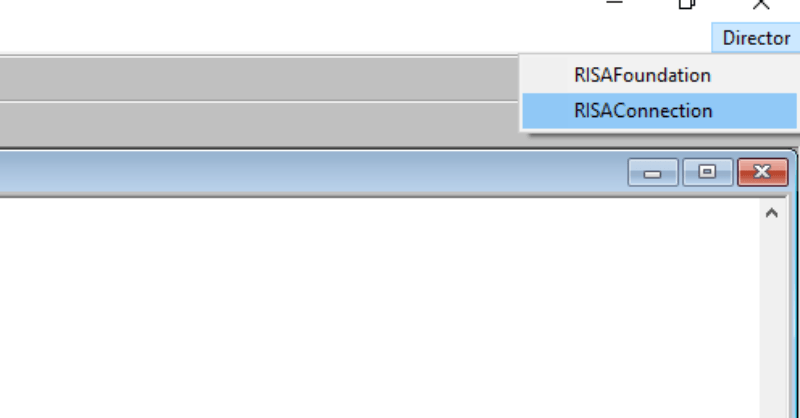
There are several ways to take your RISA-3D or RISAFloor model to...
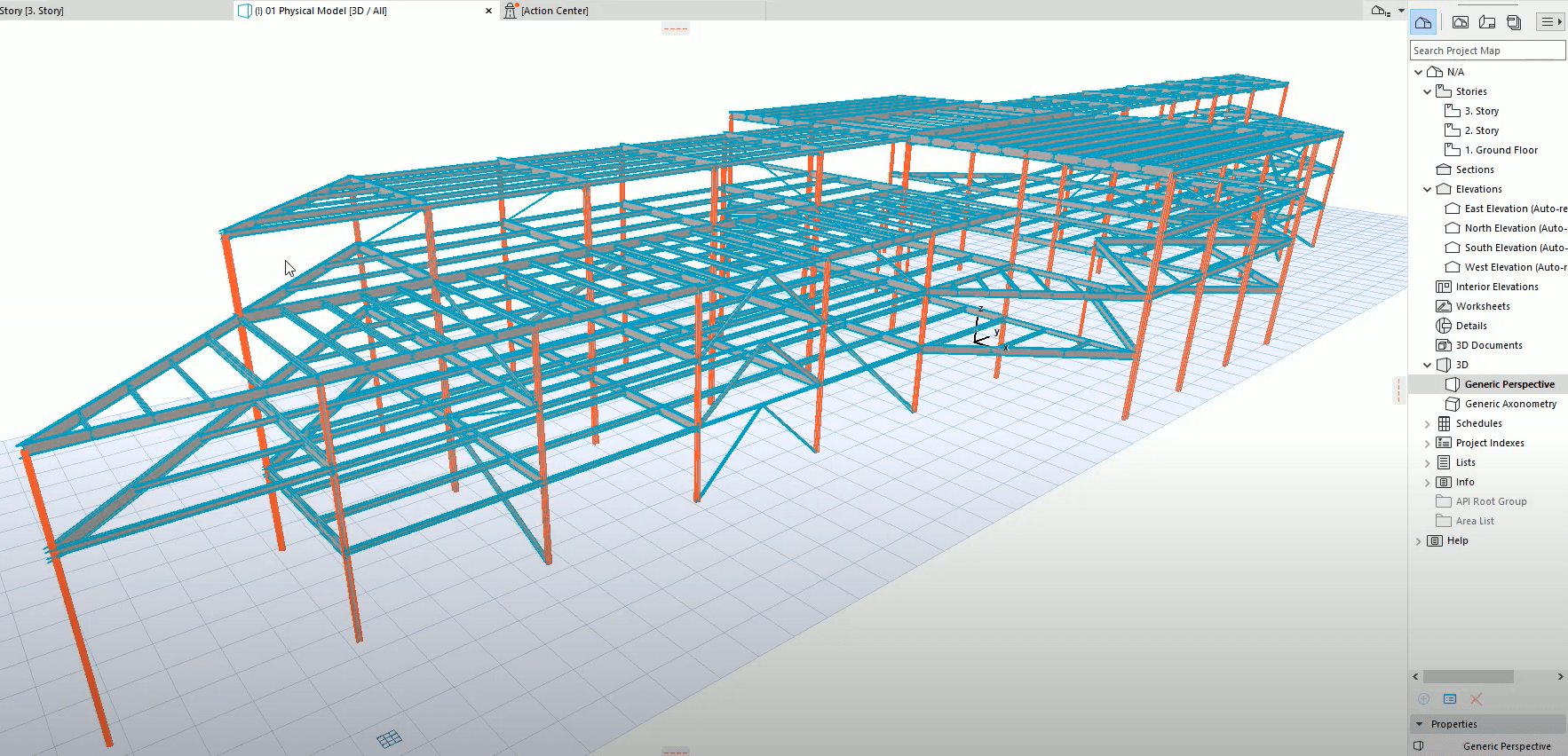
RISA is pleased to announce the release of the new RISA-Archicad...
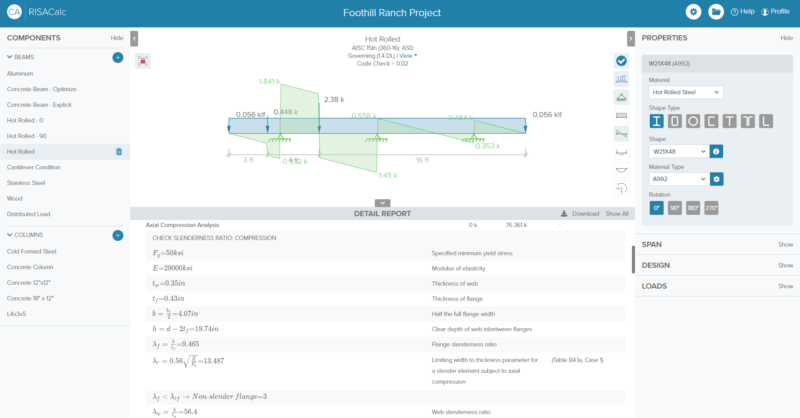
The new RISACalc allows users to analyze single members (beams and...